Energy Storage System using Solid mass gravitational
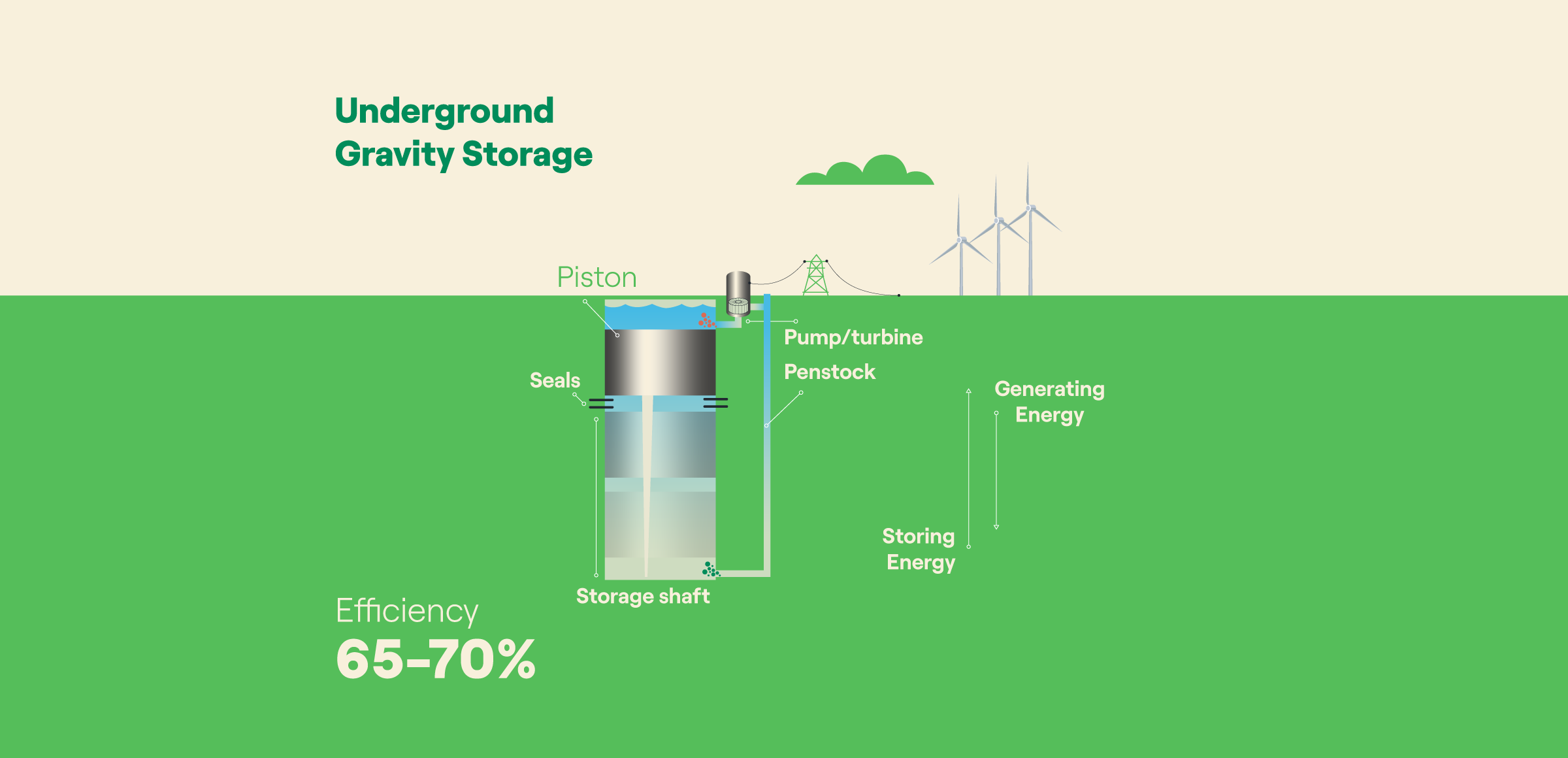
Solid Gravitational Energy Storage (SGES) operates on the same basic principles as all gravitational energy storage systems. It uses solid materials, such as concrete, to store and release energy by raising and lowering heavy blocks vertically, thereby storing and releasing gravitational potential energy.
The system consists of a series of lifting mechanisms powered by electric motors—similar to freight elevators—that raise large bricks or concrete blocks and then lower them in a controlled manner, thereby recovering the previously stored energy.
Advantages:
Long Lifespan:
Solid objects do not wear out easily and can store energy for long periods without degradation.Flexibility:
These systems can be implemented at various scales and with different materials.Stability:
SGES offers a relatively stable and reliable method of energy storage.
Limitations:
High Initial Cost:
Building and deploying these systems require specific infrastructure, which can be expensive.Low Efficiency:
The energy conversion efficiency is generally lower than that of other storage methods due to losses during various processes.Space Requirements:
These systems need a significant amount of space to lift and lower the heavy materials.
Applications:
Solar and Wind Energy Systems:
To store excess energy produced during low-demand periods and use it during peak demand times.Electric Grids:
For grid stabilization and to prevent fluctuations and outages.Microgrid Systems:
To supply energy to remote areas and islands.


0 Comments