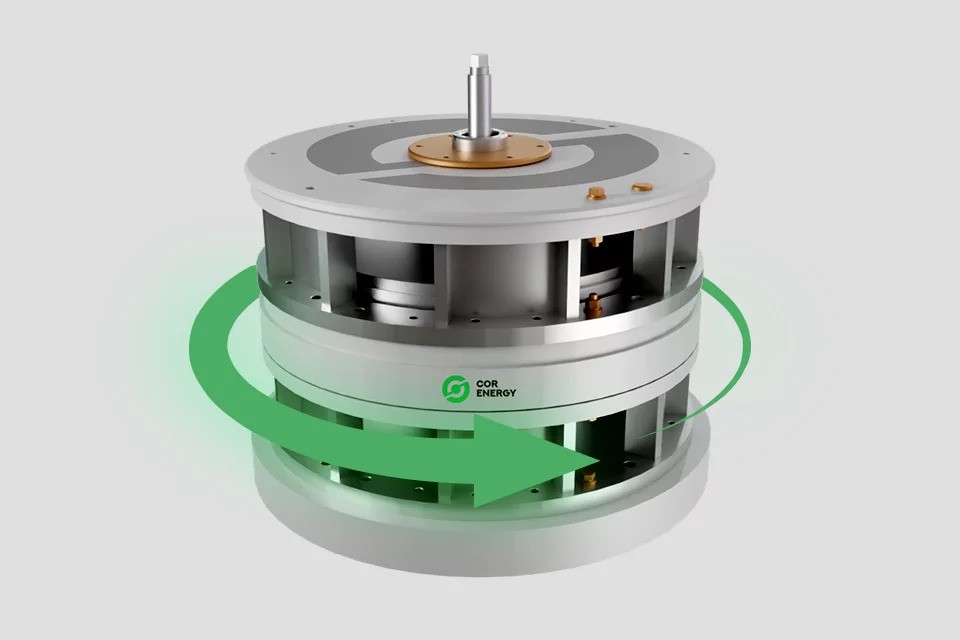

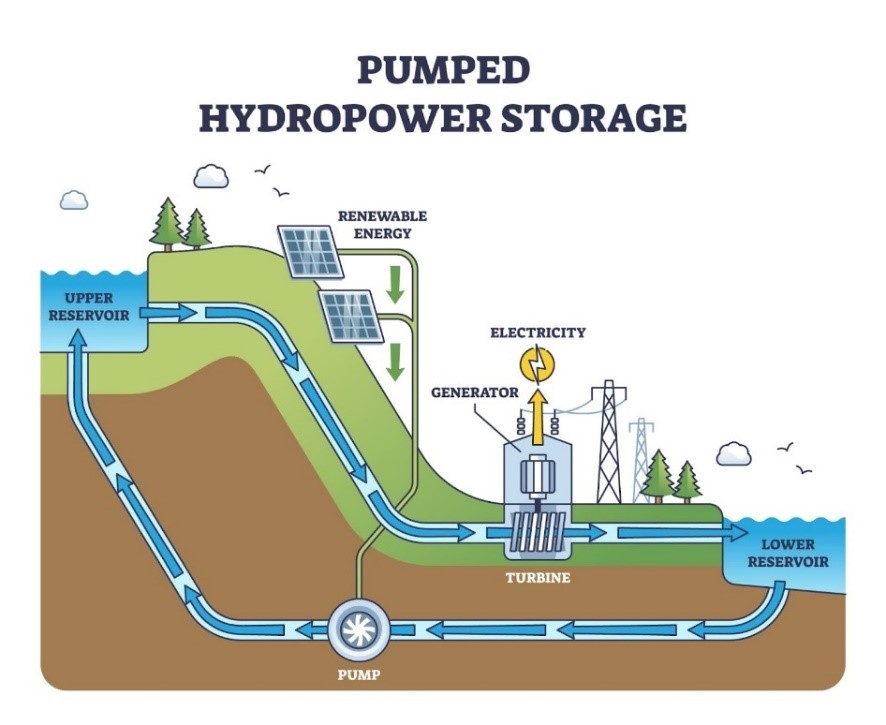
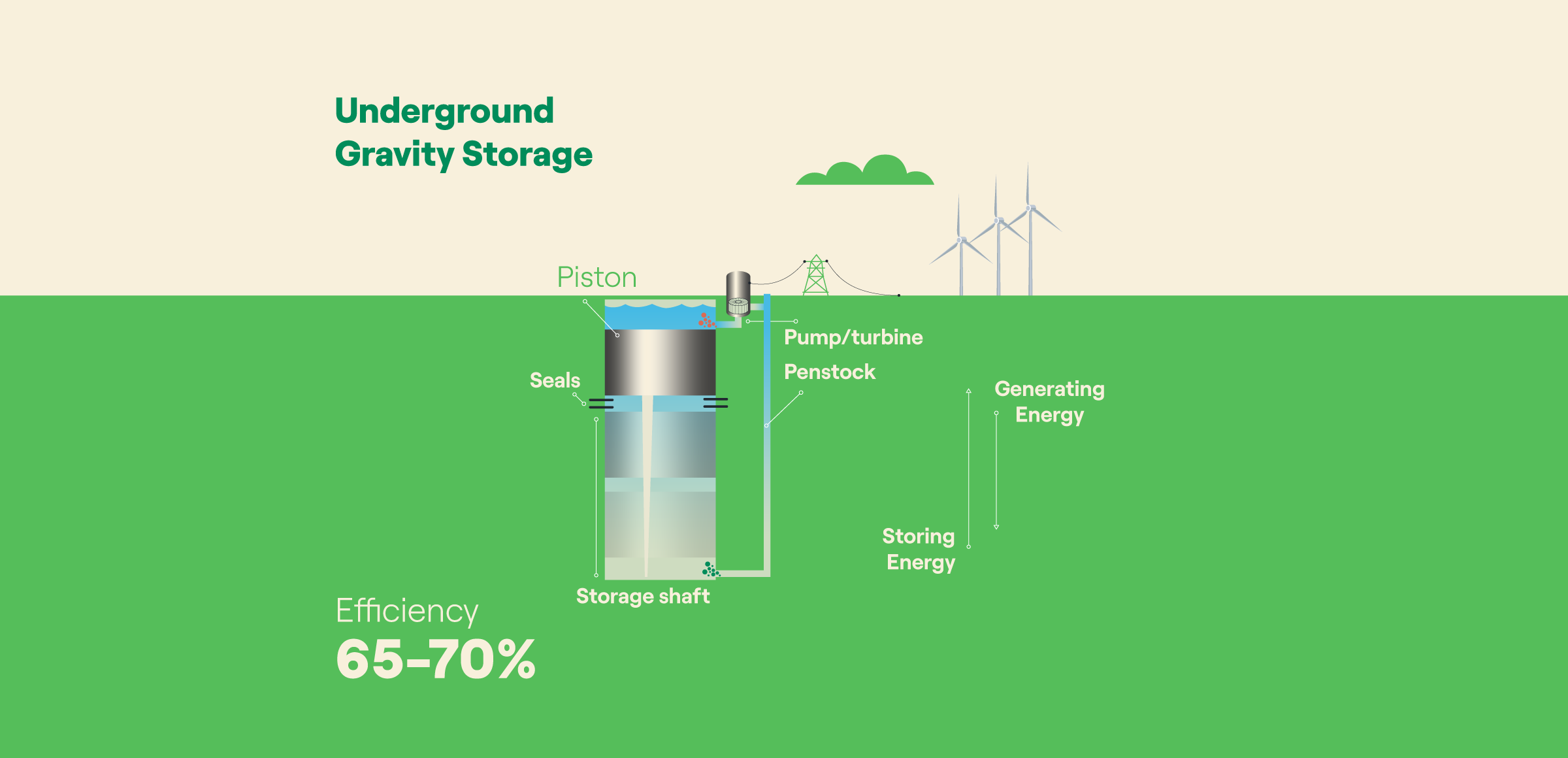
Energy Storage using Fly Wheel
The flywheel, or "flywheel energy storage," is a novel and efficient method for storing energy. In this method, electrical energy is converted into kinetic energy and stored in a heavy, highly durable rotor known as a flywheel.
How the Flywheel Works:
Storage:
When there is excess energy in the system, an electric motor spins the flywheel at a very high speed. The kinetic energy of the spinning flywheel stores the energy much like a large battery.Release:
When energy is needed, the flywheel is connected to a generator. By slowing down the flywheel's rotation, the stored kinetic energy is converted back into electrical energy and injected into the power grid.
Advantages:
High Energy Density:
Flywheels can store a large amount of energy in a relatively small volume.Rapid Response:
Flywheels can quickly store and release energy, making them very useful for applications that require fast response times.Long Lifespan:
With high-quality materials and proper design, flywheels can operate for a very long time.Environmentally Friendly:
Flywheels produce no pollution and are very clean in terms of environmental impact.Quick Charging Capability:
The flywheel can be charged in a short period of time.
Limitations:
High Cost:
The construction and maintenance of flywheels are expensive due to the need for high-quality materials and advanced control systems.Energy Loss:
Some energy is lost due to friction and air resistance during the flywheel's rotation.Size and Weight:
Flywheels are generally large and heavy, which can impose limitations for certain applications.
Applications:
Power Industry:
Used for grid stabilization, renewable energy management, and peak load reduction.Electric Vehicles:
Enhance acceleration and extend the driving range of electric cars.Residential Energy Storage:
Store energy produced by solar panels.UPS Systems:
Provide emergency power during outages.

0 Comments