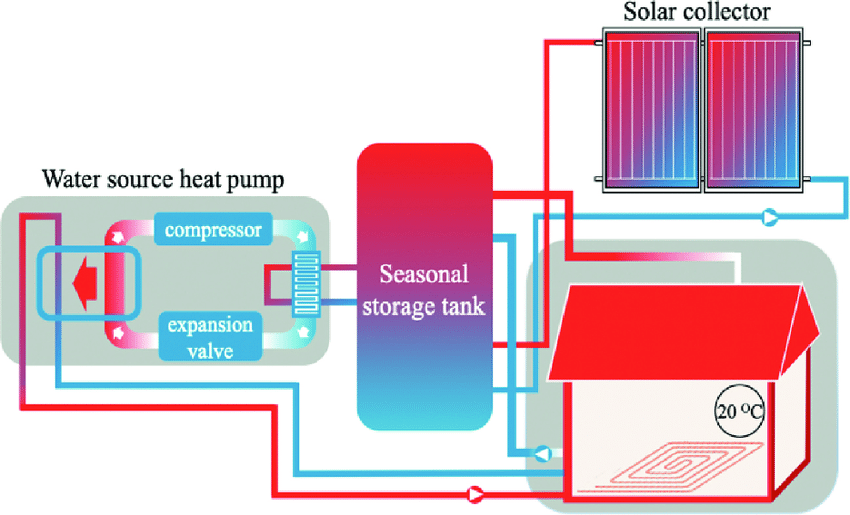
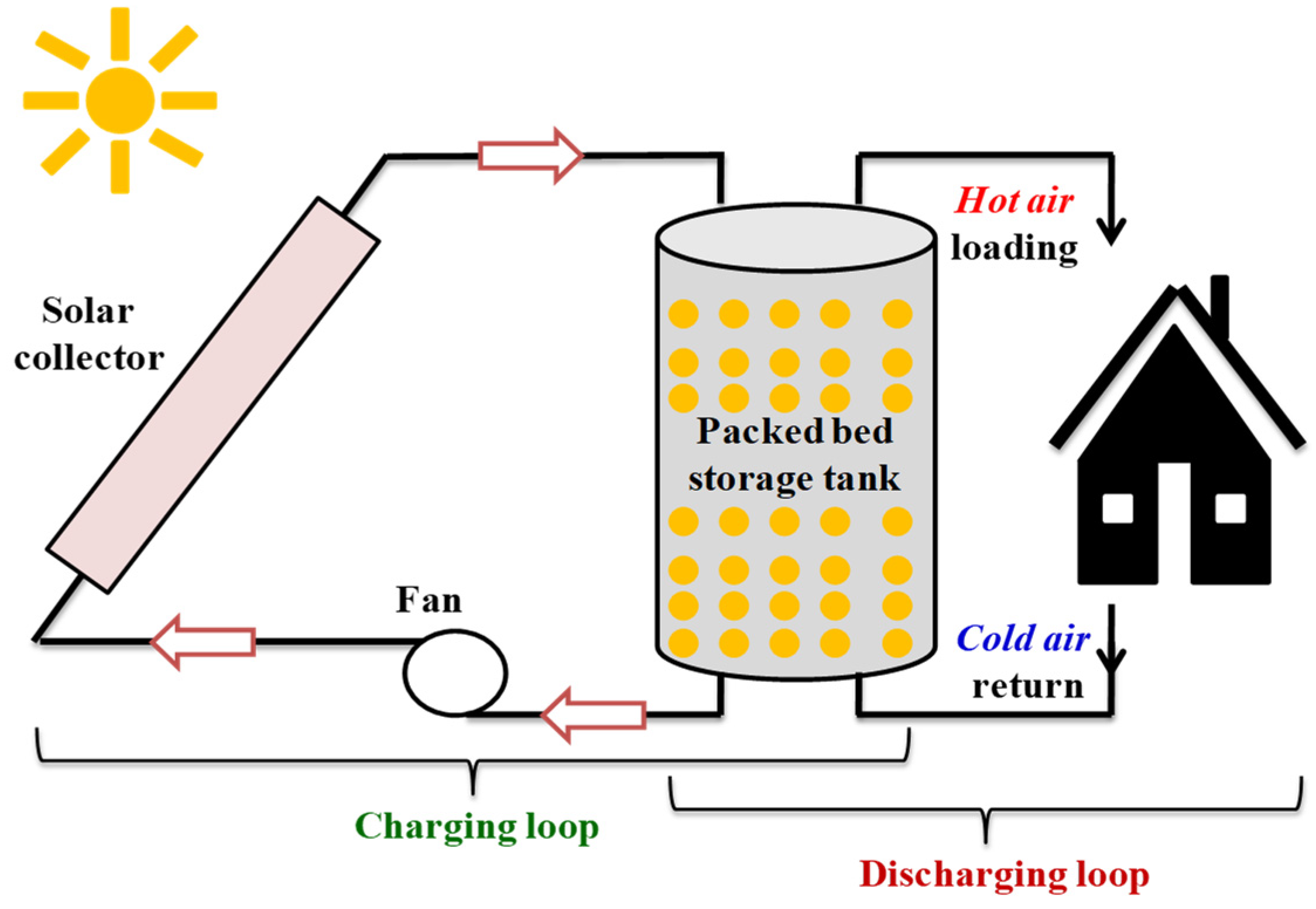
Thermal Energy Storage
Thermal Energy Storage (TES) refers to the temporary storage or release of heat.
Sensible Heat Storage
Sensible heat storage is one of the most common methods of thermal energy storage. In this approach, thermal energy is stored by increasing the temperature of a material. Unlike latent heat storage, where energy is stored during a phase change, sensible heat storage relies on temperature changes without a change in the material’s phase.
When heat is applied to a material, its temperature rises, indicating an increase in its internal energy. In sensible heat storage, this added energy is stored within the material and can be released when needed. For example, heated water stored in a tank retains thermal energy in the form of sensible heat.
Advantages:
Simplicity:
Sensible heat storage systems are usually simpler and more cost-effective than latent heat storage systems.Variety of Materials:
A wide range of materials can be used for sensible heat storage, including water, rocks, metals, and certain fluids.Temperature Control:
Energy can be easily stored and released by controlling the temperature of the storage material.
Limitations:
Lower Energy Density:
Compared to latent heat storage, sensible heat storage has a lower energy density. In other words, a larger volume of material is needed to store the same amount of energy.Heat Loss:
Proper insulation is required to prevent heat loss and maintain the temperature of the storage material.
Applications:
Heating Systems:
Storing hot water for use in building heating systems.Industry:
Storing heat for industrial processes such as metal melting.Solar Energy:
Storing heat collected from the sun for use during nighttime.
Common Materials Used:
Water:
The most widely used material for sensible heat storage due to its high heat capacity and widespread availability.Rock and Concrete:
Used in buildings for heat storage due to their high heat capacity and low cost.Metals:
Metals such as iron and aluminum are used in specific applications due to their high thermal conductivity.Oils and Molten Salts:
Used at high temperatures for storing thermal energy.

0 Comments